快速排序算法
快速排序是一种高效的排序算法,它基于将数据阵列划分为更小的数组。一个大型数组被分成两个数组,其中一个数组的值小于指定的值,比如pivot,根据该数组创建分区,另一个数组保存的值大于数据透视值。
快速排序对数组进行分区,然后递归调用两次以对两个结果子数组进行排序。该算法对于大尺寸数据集非常有效,因为其平均和最差情况复杂度为0(n 2),其中 n 是项目数。
快速排序中的分区
以下动画表示解释了如何在数组中查找透视值。
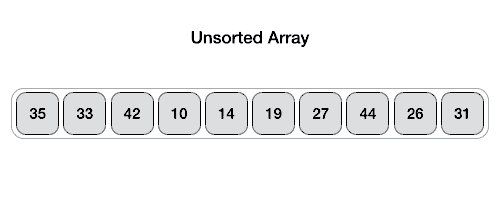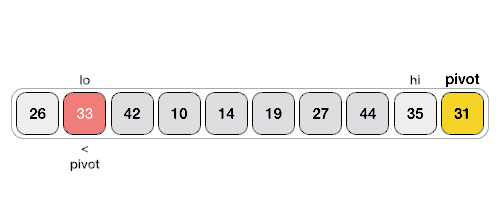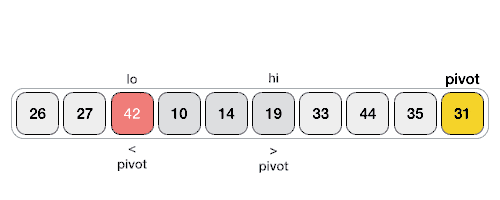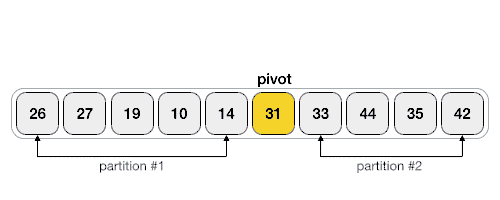
数据透视值将列表分为两部分。并且递归地,我们找到每个子列表的轴,直到所有列表只包含一个元素。
快速排序枢轴算法
基于我们对快速排序中的分区的理解,我们现在将尝试为其编写算法,如下所示。
**Step 1** − Choose the highest index value has pivot **Step 2** − Take two variables to point left and right of the list excluding pivot **Step 3** − left points to the low index **Step 4** − right points to the high **Step 5** − while value at left is less than pivot move right **Step 6** − while value at right is greater than pivot move left **Step 7** − if both step 5 and step 6 does not match swap left and right **Step 8** − if left ≥ right, the point where they met is new pivot
Quick Sort Pivot Pseudocode
上述算法的伪代码可以推导为
function partitionFunc(left, right, pivot)
leftPointer = left
rightPointer = right - 1
while True do
while A[++leftPointer] < pivot do
//do-nothing
end while
while rightPointer > 0 && A[--rightPointer] > pivot do
//do-nothing
end while
if leftPointer >= rightPointer
break
else
swap leftPointer,rightPointer
end if
end while
swap leftPointer,right
return leftPointer
end function
快速排序算法
递归地使用pivot算法,我们最终得到更小的可能分区。然后处理每个分区以进行快速排序。我们为quicksort定义递归算法如下 -
**Step 1** − Make the right-most index value pivot **Step 2** − partition the array using pivot value **Step 3** − quicksort left partition recursively **Step 4** − quicksort right partition recursively
快速排序伪代码
要了解更多信息,请参阅伪代码以进行快速排序算法
procedure quickSort(left, right)
if right-left <= 0
return
else
pivot = A[right]
partition = partitionFunc(left, right, pivot)
quickSort(left,partition-1)
quickSort(partition+1,right)
end if
end procedure